Pollaste is a term gaining recognition across various industries due to its unique applications and benefits. Whether you’re in agriculture, food production, or environmental science, pollaste has a vital role to play. This guide delves into what it is, its key applications, and the benefits that make it stand out. We’ll also explore how it is being used globally to drive innovation and sustainability.
What is Pollaste?
It is an organic byproduct commonly sourced from poultry farms. It is the residual matter, including feathers, manure, and bedding, typically generated in large quantities by poultry operations. Historically, It was treated as waste, but advancements in technology and research have uncovered its potential uses. Now, it’s being repurposed across a variety of sectors, from organic farming to bioenergy production.

Key Benefits
The growing interest in it is largely due to its numerous benefits. These benefits are particularly appealing in fields focused on sustainability and eco-friendly practices. Below are the key advantages of pollaste:
- Nutrient-Rich Fertilizer
One of the primary uses of pollaste is as a natural fertilizer. It contains a high concentration of essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are vital for plant growth. These nutrients are released slowly into the soil, enhancing its fertility without the harsh environmental impacts associated with synthetic fertilizers. - Cost-Effective Resource
For farmers and industries, pollaste offers a cost-effective alternative to more expensive raw materials. As it is a byproduct of poultry farming, its availability is vast and relatively inexpensive to acquire. By turning waste into a valuable resource, it helps cut costs and supports circular economies. - Reduction in Greenhouse Gases
Utilizing it helps reduce methane and carbon dioxide emissions, which are major contributors to global warming. When it is properly managed and repurposed, it prevents these harmful gases from entering the atmosphere, promoting a more sustainable ecosystem. - Soil Improvement
In addition to providing essential nutrients, it improves soil structure. It enhances the soil’s ability to retain moisture and promotes healthy microbial activity, which in turn supports the growth of plants and increases agricultural yield.
Applications of Pollaste in Various Industries
While it is predominantly used in agriculture, its applications are not limited to farming. Innovations in processing and technology have made it a versatile material. Let’s explore some of the notable uses:
1. Organic Farming
Organic farming is one of the primary sectors benefiting from pollaste. As an organic fertilizer, it aligns perfectly with the principles of sustainable agriculture, reducing the reliance on chemical fertilizers. Farmers who adopt pollaste report improved crop yields, healthier soil, and lower costs associated with fertilization.
2. Bioenergy Production
Pollaste is also gaining traction in bioenergy production. Through anaerobic digestion, pollaste can be converted into biogas, a renewable source of energy. This process not only generates electricity but also reduces the amount of waste sent to landfills, further minimizing the environmental footprint.
3. Soil Erosion Control
Pollaste is being used in projects focused on soil conservation. Its organic matter helps stabilize soil and prevent erosion, particularly in areas vulnerable to degradation. By using pollaste, land managers can create a more resilient environment that supports both plant and animal life.
4. Wastewater Treatment
Another emerging application of pollaste is in wastewater treatment. When processed, pollaste can act as a natural filtration system, helping to remove impurities and improve the overall quality of water. This is particularly beneficial in rural areas where access to advanced water treatment facilities is limited.
The Future of Pollaste: Trends and Innovations
As the demand for sustainable and eco-friendly practices continues to rise, the potential uses of pollaste are expanding. Ongoing research is focusing on improving the efficiency of pollaste processing techniques, making it even more accessible and effective for a variety of uses.
One exciting trend is the development of pollaste-based biochar, a carbon-rich material that can sequester carbon from the atmosphere while enhancing soil health. Another trend is its potential use in creating biodegradable packaging materials, offering a greener alternative to plastics.
Table: Nutrient Composition of Pollaste
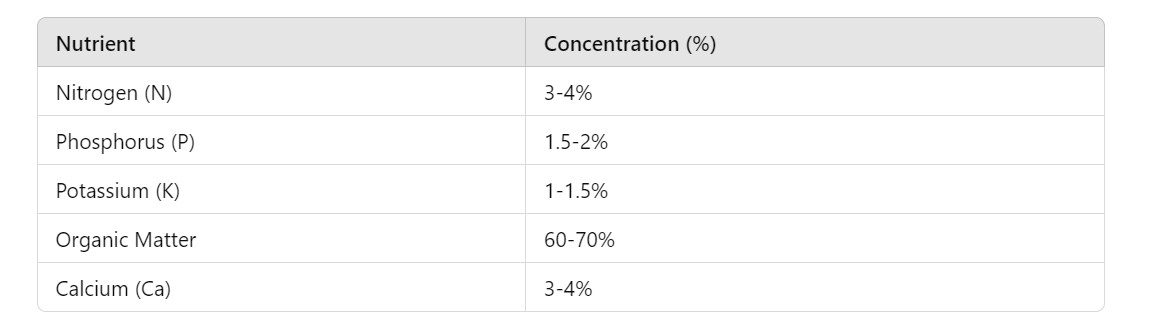
Description: The table above shows the nutrient composition of pollaste. These values indicate its high nutrient content, particularly in nitrogen and organic matter, which make it ideal for use as a fertilizer.
Conclusion
Pollaste is no longer just a byproduct of poultry farming—it’s a valuable resource with significant benefits across industries. From its role in organic farming to its use in energy production and soil conservation, pollaste is driving innovation and sustainability. As the world looks for more eco-friendly solutions, pollaste offers a cost-effective and environmentally conscious option. Embracing pollaste in various applications not only helps reduce waste but also supports long-term ecological balance.
By continuing to explore and invest in pollaste-based technologies, we can unlock even more potential, making pollaste a key player in the global push toward sustainability.

FAQs
1. What is it used for?
It is primarily used as an organic fertilizer, but it also has applications in bioenergy production, soil erosion control, and wastewater treatment.
2. How does it benefit agriculture?
It enhances soil fertility, improves moisture retention, and supports healthier crop yields, making it an ideal choice for sustainable agriculture.
3. Can it help reduce greenhouse gases?
Yes, repurposing it prevents the release of methane and carbon dioxide, which are major contributors to climate change.
4. Is it a renewable resource?
Yes, It is a renewable byproduct of poultry farming, and its continuous availability makes it a sustainable resource.
5. How is it processed for use in bioenergy?
It is processed through anaerobic digestion, which breaks it down to produce biogas, a renewable energy source.
6. What are the environmental benefits of using it?
It helps reduce waste, lowers greenhouse gas emissions, and improves soil health, all contributing to a more sustainable environment.











