Introduction
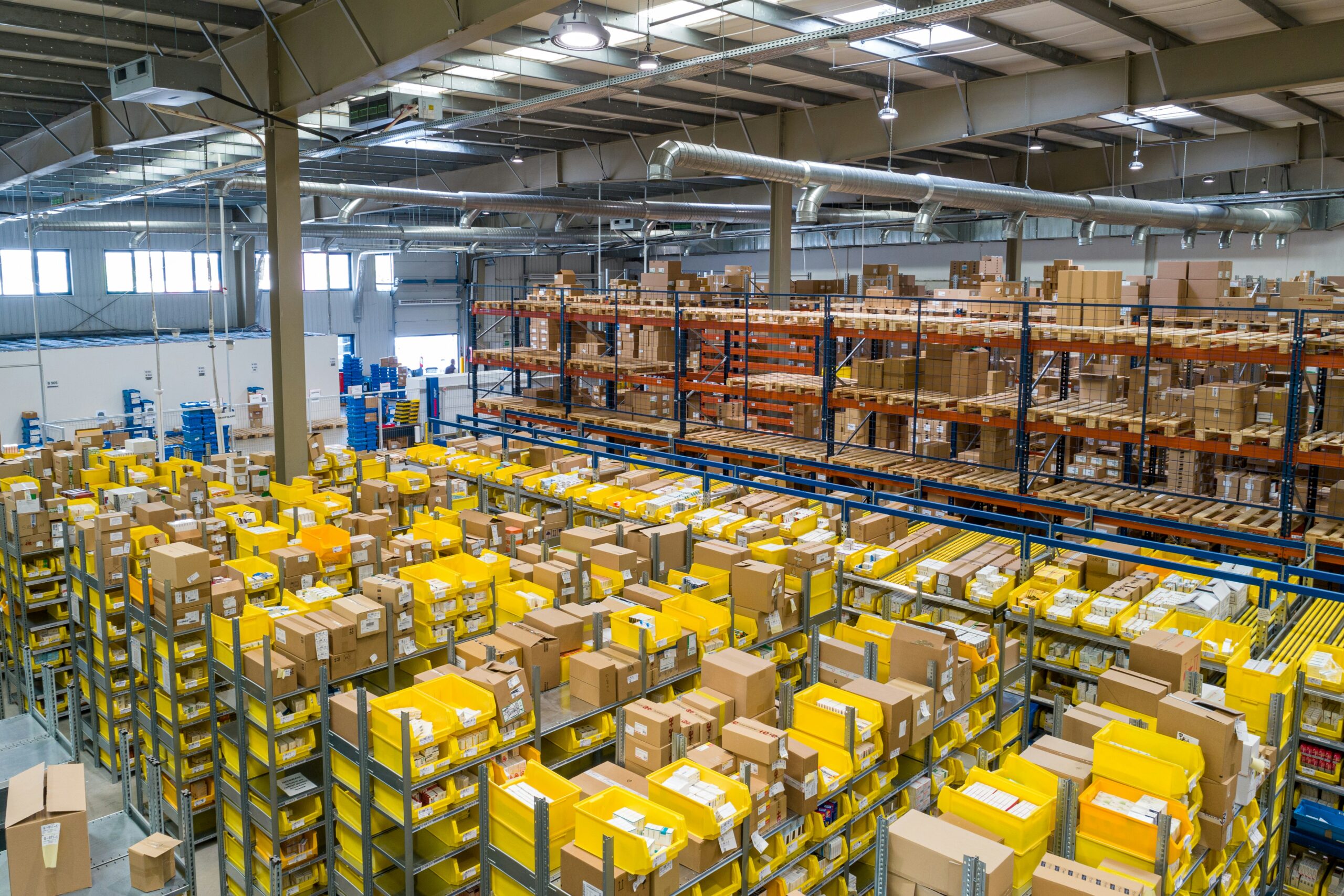
If you’re searching for a warehouse for rent, you’re tackling an important decision that can significantly impact your business operations. Whether you need storage, distribution capabilities, light manufacturing space, or a fulfillment center, the right warehouse boosts efficiency and growth. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll cover essential aspects like size, location, cost, lease terms, and amenities to help you make an informed choice.
Why Renting a Warehouse Matters
Choosing the right warehouse sets the groundwork for:
-
Business Efficiency: A well-appointed warehouse streamlines supply chain processes from receiving to shipping.
-
Cost Management: Rent is often more practical than purchasing, especially for companies seeking flexibility.
-
Scalability: Renting lets you adjust your space requirements as your business evolves.
-
Compliance: Access to proper facilities ensures you meet regulatory standards and safety requirements.
Determining Your Space Needs
1. Calculate Required Square Footage
Start by assessing your inventory volume, processing needs, and future growth. Use this formula:
Warehouse Size = (Daily Throughput × Inventory Days) + Workspace + Mezzanine
2. Consider Layout and Workflow
Make sure the warehouse supports product flow—from receiving area to storage, packing, and shipping zones.
3. Account for Amenities
Different operations demand features like high ceilings (20–30 ft), climate control, loading docks, sufficient power, and office space.
Location: Choose Smartly
Proximity to Market & Clients
Rent near your suppliers, customers, and transit hubs to reduce shipping costs and delivery times.
Access to Transportation
Look for easy access to highways, ports, airports, and rail links—ensure traffic flow won’t slow down logistics.
Zoning & Permits
Confirm the warehouse zoning matches your business needs (e.g., light industry vs. heavy manufacturing).
Local Labor Pool
Access to reliable labor can influence warehouse location—consider communities with logistics talent.
Understanding Warehouse Lease Types
1. Triple Net Lease (NNN)
You handle rent plus property taxes, insurance, and maintenance. Offers lower base rent but higher responsibility.
2. Modified Gross or Full-Service Lease
Rent covers most expenses. Budget-friendly but may cost more upfront.
3. Short-Term vs. Long-Term
Short leases provide flexibility; long leases often include options to expand and secure lower rates.
Cost Components & How to Compare
-
Base Rent: Standard monthly cost per square foot.
-
Operating Expenses: Includes utilities, maintenance, and security.
-
Common Area Maintenance (CAM): Shared spaces like driveways or bathrooms.
-
Security Deposits & Tenant Improvements (TI): One-time costs to prepare the space.
-
Escalation Clauses: Increases tied to inflation or market rent.
Always get a total occupancy cost for accurate comparison.
Must-Have Features & Build-Out Essentials
-
Loading Docks & Drive-Ins: Vital for heavy logistics operations.
-
Clear Height: 24 ft or higher supports high-rack storage systems.
-
Mezzanine Options: Great for extra office, packing, or storage space.
-
Power & Lighting: High-wattage power supports equipment; LED lighting reduces energy costs.
-
Climate Control: Necessary for perishable goods, electronics, or full-temperature-sensitive items.
-
Fire Sprinklers & Safety: Ensure compliance with local fire codes; consider OSHA requirements.
Conducting Evaluation & Inspection
-
Property Visits: Check floor flatness, drainage, roof condition, pest presence, and HVAC.
-
Environmental Check: Review Phase I Environmental Site Assessments for contamination.
-
Safety Features: Look for emergency exits, alarms, and security cameras.
-
Accessibility: Evaluate nearby road quality and traffic flow.
Negotiating Tips
-
Lease Term & Renewal: Try for 5+ years with renewal options and expansion rights.
-
Tenant Improvements: Negotiate landlord-funded fitouts like racks or offices.
-
Rent Concessions: Ask for free months or discounted introductory rent.
-
Exit & Sublease Clauses: Flexible exit terms limit risk if your needs change.
-
Escalation Cap: Cap annual rent increases to manage financial planning.
Operational & Ongoing Considerations
-
Subleasing Options: Flexibility to reduce space during downtimes.
-
Insurance Requirements: Ask your broker about coverage for liability, contents, and equipment.
-
Maintenance Responsibilities: Define who handles roof, HVAC, or structural upkeep.
-
Sustainability Incentives: Landlords may offer LEED- or energy-efficiency perks.
Conclusion
Finding the perfect warehouse for rent is a strategic move that impacts your logistics, productivity, and cost structure. Focusing on the right size, location, lease terms, and necessary amenities helps you avoid expensive surprises and operational challenges.
Next steps:
-
Outline your space and budget needs
-
Visit multiple properties and inspect carefully
-
Negotiate terms that include tenant improvements and flexibility
-
Consult industry professionals—brokers, real estate attorneys, and 3PL advisers—to support your decision